Introduction to Elevator Dimensions:
Overview of Elevator Importance in Modern Architecture:
Elevators, once a luxury, are now considered essential in modern architecture. They not only provide vertical mobility but also significantly enhance the functionality and accessibility of residential and commercial buildings.
As buildings soar higher and the demographics of societies shift towards an aging population, the role of elevators becomes even more crucial. They cater not just to convenience but also to the essential needs of individuals with limited mobility, offering them independence in navigating multi-story buildings.
Basic Understanding of Elevator Components:
To fully grasp how elevator dimensions impact design and functionality, it’s vital to understand the main components that make up an elevator system. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and safety.
- Elevator Shaft:�
Known technically as the hoistway, the elevator shaft is the vertical space dedicated to accommodating the elevator’s movement between floors. It houses the critical machinery needed to operate the elevator and must be constructed to precise dimensions to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Elevator Cab:�
The cab is the space where passengers ride. The interior can be customized with various finishes and fittings, reflecting the building’s aesthetic and functional requirements. The dimensions of the cab are critical as they determine the comfort and capacity of the elevator.
- Elevator Entrance:�
The entrance includes the doors that passengers use to access the elevator cab. The width and design of the entrance are important for accessibility. They must be wide enough to accommodate passengers, including those in wheelchairs or those needing other mobility aids, and must comply with safety regulations to ensure a smooth entry and exit.
Understanding these components helps in making informed decisions about elevator dimensions, which can significantly affect the usability and safety of the elevator system. Next, we will delve into the standard dimensions and regulations that govern the construction and modification of elevators, ensuring they meet current needs and safety standards.
Standard Elevator Dimensions and Regulations:
Exploring Standard Elevator Dimensions:
Understanding standard elevator dimensions is crucial for architects, builders, and homeowners alike. Here are some common configurations:
- Residential Elevators:�
Typically, these are smaller than commercial elevators. A standard residential elevator might measure 36 inches (3 feet) wide by 48 inches (4 feet) deep. These dimensions make it easier to integrate an elevator into an existing home without significant renovations.
- Commercial Elevators:�
In commercial settings, elevators need to accommodate a higher volume of traffic and more varied use cases. As such, they are generally larger. Standard dimensions might range from 6.5 to 7 feet wide by 6 feet deep, which allows more people to move comfortably at the same time.
Regulatory Standards for Elevator Dimensions:
Compliance with local and international safety and accessibility standards is non-negotiable for elevator installation. Here are some key regulations:
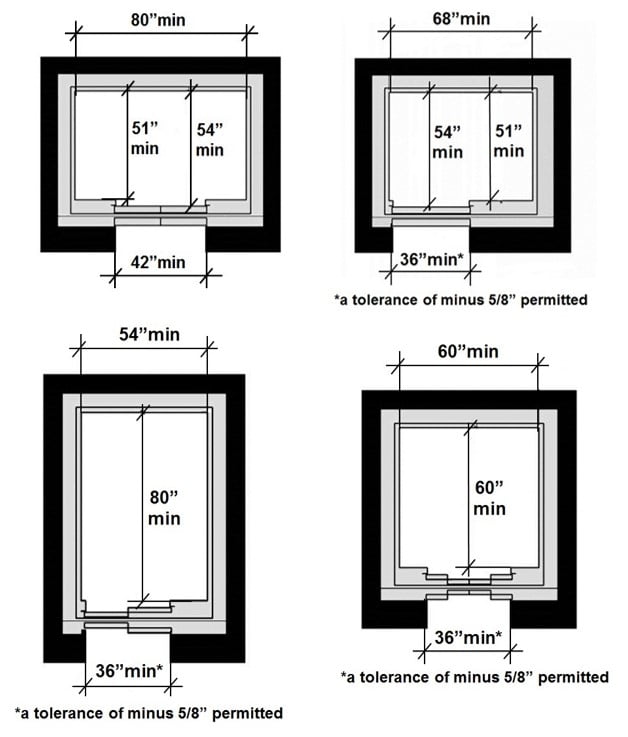
- ADA Standards for Accessible Design:�
In the United States, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provides guidelines to ensure that elevators are accessible to everyone. ADA standards specify minimum internal elevator dimensions, door width, and arrangement to accommodate passengers with disabilities, including those in wheelchairs.
- International Standards and Regional Variations:�
Different countries and regions have their own standards. For instance, the Ontario Building Code in Canada requires elevators in buildings higher than three stories to accommodate a stretcher measuring 2010 mm by 610 mm. These regulations ensure that elevators are safe and accessible to all users, regardless of their physical abilities.
Understanding these dimensions and regulations is essential not only for compliance but also for ensuring that elevators provide safe, efficient, and comfortable transportation for all users.
Advanced Elevator Technologies and Customization:
Innovative Elevator Types and Their Dimensions:
As technology advances, so do elevator designs, leading to more sophisticated and tailored solutions that meet specific architectural and user needs. Here are some innovative types of elevators:
- Pneumatic Vacuum Elevators (PVE):�
These elevators use air pressure as the lifting mechanism and are known for their compact and versatile designs. The PVE30, for example, has an exterior diameter of just 750 mm and is perfect for single-passenger transport. The larger PVE52, with an exterior diameter of 1316 mm, can accommodate three passengers or a wheelchair, showcasing the flexibility in size and capacity within the same technology.
- Customizable Elevator Systems:�
Modern elevators can be fully customized not only in terms of dimensions but also features and aesthetics. Whether it’s adjusting the size to fit a specific building design or incorporating advanced features like touchless controls and customized interiors, elevators now can truly reflect the unique needs and styles of their environments.
Read More: 5 TIPS TO MAINTAIN AN ELEVATOR
Practical Considerations for Elevator Installation:
Installing an elevator involves several practical considerations to ensure it adds value and functionality to the building:
- Space Requirements:�
The required space for an elevator goes beyond the shaft and car dimensions. It includes additional machinery and equipment spaces, especially for systems like hydraulic or traction elevators which might need separate machine rooms.
- Architectural Integration:�
Elevators should seamlessly integrate with the building’s design. This requires careful planning from the outset of building design, especially for glass or panoramic elevators that can serve as architectural focal points.
- Safety and Accessibility:�
Safety is paramount in elevator design. This includes adhering to international safety standards and local codes. Accessibility considerations must ensure that all users, including those with disabilities, can use the elevator safely and comfortably.
Conclusion:
Elevator dimensions are a critical aspect of both design and functionality in modern architecture. With advancements in technology, the range of available options has expanded, allowing for customization and innovation in elevator design. As buildings evolve and accessibility becomes even more crucial, understanding and implementing the right elevator dimensions and technologies will continue to be essential.
FAQs:
- What are the standard dimensions of a residential elevator?
Most residential elevators are approximately 3 feet wide by 4 feet deep, but dimensions can vary based on the model and customization options. - How much space is needed to install an elevator in a home?
In addition to the footprint of the elevator itself, extra space may be required for components like the machine room, unless a machine-room-less (MRL) elevator is used. - What are the ADA requirements for elevator dimensions?
The ADA requires elevators to have a minimum door width of 36 inches and enough internal space to accommodate a wheelchair, typically around 54 inches by 68 inches inside. - Can elevators be customized for small residential buildings?
Yes, elevators can be highly customized in terms of size, technology, and interior finishes to fit even in small residential buildings. - What are the latest trends in elevator technology and design?
Recent trends include the use of smart elevator technology, integration of IoT for better maintenance and service, and designs that contribute to building aesthetics, such as glass or panoramic elevators.

